Dice games have been popular for centuries, and rolling dice is a fundamental part of many board games and tabletop role-playing games. In this blog, we'll explore a simple Python program that simulates rolling a 6-sided die and displays the result using ASCII art. This entertaining project can be a fun addition to your Python coding repertoire and is a great way to practice your programming skills.
Github link:
terminal-dice-roller
The Code:
Let's break down the code step by step.
- Dice Art: ```python
DICE_ART = {
1: (
"┌─────────┐",
"│ │",
"│ ● │",
"│ │",
"└─────────┘",
),
# ... (similar entries for values 2 to 6)
}
This dictionary (`DICE_ART`) contains ASCII art representations of the six faces of a standard six-sided die. Each face is represented as a tuple of strings, which will be used later to display the dice face when rolled.
2. **Constants**:
```python
DIE_HEIGHT = len(DICE_ART[1])
DIE_WIDTH = len(DICE_ART[1][0])
DIE_FACE_SEPARATOR = " "
These constants define the height and width of a die face and the separator character used between multiple dice faces when displayed.
-
roll_dice()Function: ```python
def roll_dice():
"""Simulate rolling a 6-sided die and return the result."""
return random.randint(1, 6)
The `roll_dice()` function generates a random integer between 1 and 6 to simulate rolling a standard six-sided die.
4. **`display_dice(die_value)` Function**:
```python
def display_dice(die_value):
"""Display the ASCII art for the given die value."""
if die_value in DICE_ART:
die_face = DICE_ART[die_value]
for line in die_face:
print(line)
This function takes the result of rolling the die and displays the corresponding ASCII art representation. It checks if the provided die_value exists in the DICE_ART dictionary and prints the associated art line by line.
-
main()Function: ```python
def main():
print("Welcome to the Dice Rolling Simulator!")
while True:
user_input = input("Press Enter to roll the dice or 'q' to quit: ").strip()
if user_input == 'q':
print("Goodbye!")
break
if user_input == '':
die_value = roll_dice()
display_dice(die_value)
else:
print("Invalid input. Press Enter to roll or 'q' to quit.")
The `main()` function serves as the entry point of the program. It displays a welcome message and enters a loop that waits for user input. The user can press Enter to roll the dice or 'q' to quit. It handles user input validation and calls the appropriate functions.
6. **`if __name__ == "__main__":`**:
This conditional statement ensures that the `main()` function is executed only if the script is run directly, not if it's imported as a module into another script.
**Example**
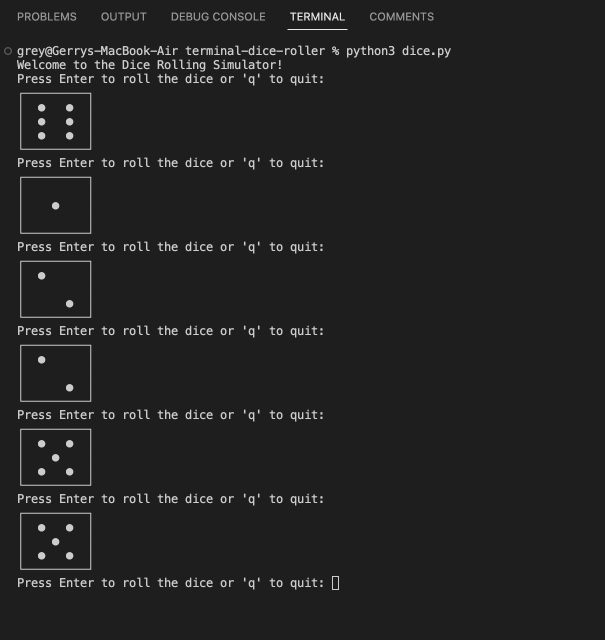
**Attention**
You can further enhance this project by adding features like keeping track of the roll history or integrating it into a larger game. You can contribute to this [repo](https://github.com/Gerry-Aballa/terminal-dice-roller) by implementing these. Happy coding and rolling!


Top comments (1)
I just checked out your post about the Python dice-rolling simulator, and I think it’s a fantastic project! Rolling virtual dice is such a fun way to practice programming skills. It’s like bringing some game night excitement to your screen. You can customize it, too—maybe add some cool features like different types of dice or even save the results for a game later.
Using simple functions to simulate the rolls can help you learn a lot about randomness in programming. If you ever want to share your code or get feedback, I’d be all in. If you're interested, you can check out more ideas about virtual dice online; tons of resources might spark some creativity.
Some comments may only be visible to logged-in visitors. Sign in to view all comments.