ABSTRACT
This project will be very useful as it will save time and effort of typing from an image. Image processing is often viewed as arbitrarily manipulating an image to achieve an aesthetic standard or to support a preferred reality. However, image processing is more accurately defined as a means of translation between the human visual system and digital imaging devices.
Python-tesseract is an optical character recognition (OCR) tool for python. That is, it will recognize and “read” the text embedded in images. Python-tesseract is a wrapper for Google’s Tesseract-OCR Engine. Tesseract developed from OCRopus model in Python which was a fork of a LSMT in C++, called CLSTM.
Tesseract library is shipped with a handy command-line tool called tesseract. We can use this tool to perform OCR on images and the output is stored in a text file.
Using the Pytesseract library in Python, we made an image processing of a photo given as input..
Scope: This application could be time-saving for giant organizations which will fetch the text from images. It can open the world of “paperless documentation” which also helps to upgrade the storage. It can also help in the automation process as it can fetch the text from the images themselves.
Table of Contents
1-) Introduction
2-) Methodology / System Design
3-) Results
LIST OF FIGURES
1. Introduction
Image Processing with the Tesseract Library Python-Tesseract is an optical character recognition (OCR) tool for python. That is, it will recognize and “read” the text embedded in images. Tesseract — an open-source OCR engine that has gained popularity among OCR developers. Even though it can be painful to implement and modify sometimes, there weren’t too many free and powerful OCR alternatives on the market for the longest time. Tesseract began as a Ph.D. research project in HP Labs, Bristol. It gained popularity and was developed by HP between 1984 and 1994. In 2005 HP released Tesseract as an open-source software. Since 2006 it is developed by Google. Tesseract is an open source text recognition (OCR) Engine, available under the Apache 2.0 license. It can be used directly, or (for programmers) using an API to extract printed text from images. It supports a wide variety of languages. Tesseract doesn’t have a built-in GUI, but there are several available from the 3rdParty page. Tesseract is compatible with many programming languages and frameworks through wrappers that can be found here. It can be used with the existing layout analysis to recognize text within a large document, or it can be used in conjunction with an external text detector to recognize text from an image of a single text line.
Installing Tesseract
tesseract –version
pip install pytesseract
pip install opencv-python
If we want to integrate Tesseract in our Python code, we will use Tesseract’s API.
tesseract image_path stdout
To write the output text in a file:
tesseract image_path text_result.txt
Pytesseract is a wrapper for Tesseract-OCR Engine. It is also useful as a stand-aloneinvocation script to tesseract, as it can read all image types supported by the Pillow and Leptonica imaging libraries, including jpeg, png, gif, bmp, tiff, and others.
The script below will give you bounding box information for each character detected by tesseract during OCR.
import cv2
import pytesseract
img = cv2.imread(‘image.jpg’)
h, w, c = img.shape
boxes = pytesseract.image_to_boxes(img)
for b in boxes.splitlines():
b = b.split(‘ ‘)
img = cv2.rectangle(img, (int(b[1]), h — int(b[2])), (int(b[3]), h — int(b[4])), (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.imshow(‘img’, img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
If we want boxes around words instead of characters, the function image_to_data will come in handy. There are several ways a page of text can be analysed. The tesseract api provides several page segmentation modes if you want to run OCR on only a small region or in different orientations, etc.
• Orientation and script detection (OSD) only.
• Automatic page segmentation with OSD.
• Automatic page segmentation, but no OSD, or OCR.
• Fully automatic page segmentation, but no OSD. (Default)
• Assume a single column of text of variable sizes.
• Assume a single uniform block of vertically aligned text.
• Assume a single uniform block of text.
• Treat the image as a single text line.
• Treat the image as a single word.
• Treat the image as a single word in a circle.
• Treat the image as a single character.
• Sparse text. Find as much text as possible in no particular order.
• Sparse text with OSD.
To change your page segmentation mode, change the — psm argument in your custom config string to any of the above mentioned mode codes.
2. METHODOLOGY / SYSTEM DESIGN
Tesseract works best when there is a clean segmentation of the foreground text from the background. In practice, it can be extremely challenging to guarantee these types of setup. There are a variety of reasons you might not get good quality output from Tesseract like if the image has noise on the background. The better the image quality (size, contrast, lightning) the better the recognition result. It requires a bit of preprocessing to improve the OCR results, images need to be scaled appropriately, have as much image contrast as possible, and the text must be horizontally aligned. Tesseract OCR is quite powerful but does have the following limitations.
• The OCR is not as accurate as some commercial solutions available to us.
• Doesn’t do well with images affected by artifacts including partial occlusion, distorted perspective, and complex background.
• It is not capable of recognizing handwriting.
• It may find gibberish and report this as OCR output.
• If a document contains languages outside of those given in the -l LANG arguments, results may be poor.
• It is not always good at analyzing the natural reading order of documents. For example, it may fail to recognize that a document contains two columns, and may try to join text across columns.
• Poor quality scans may produce poor quality OCR.
• It does not expose information about what font family text belongs to.
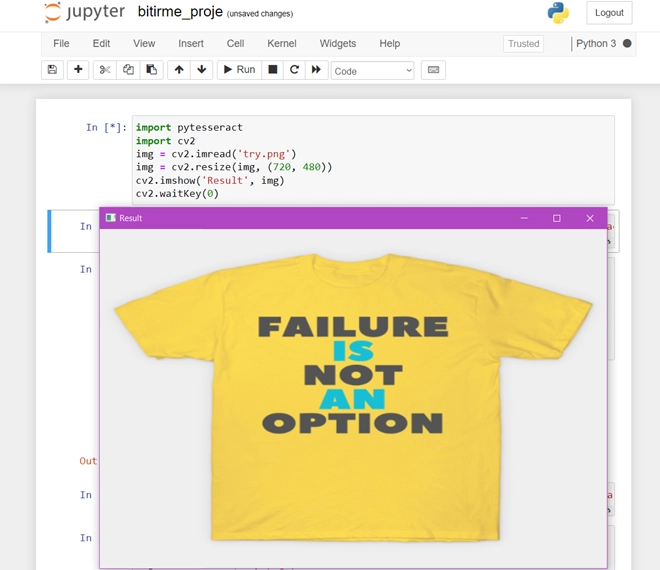
OPENING A SIMPLE IMAGE
- Import cv2.
- Import pytesseract.
- Save the test image in the same directory.
- Create a variable to store the image using cv2.imread() function and pass the name of the image as parameter.
- To resize the image use cv2.resize() function and pass the required resolution.
- Use cv2.imshow(‘window_name’, image_name).
- Add a cv2.waitKey(0) to display image for infinity.
CONVERTING IMAGE TO STRING
- Import cv2, pytesseract.
- Save the test image in the same directory.
- Create a variable to store the image using cv2.imread() function and pass the name of the image as parameter.
- Use cv2.imshow(‘window_name’, Image_name).
- To convert to string use pytesseract.image_to_string(‘image_name’) and store it in a variable.
- Print the string.
- Add a cv2.waitKey(0) to display image for infinity.
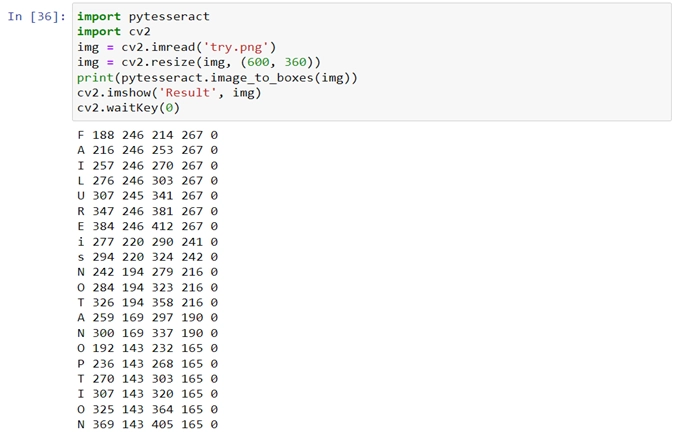
PRINTING THE EXACT POSITION OF TEXT/NUMBERS
image_to_boxes() function creates imaginary boxes around each text and returns four values for each character, which are as follows:
a) x coordinate.
b) y coordinate.
c) diagonal point of x coordinate.
d) Diagonal point of y coordinate
- Import cv2, pytesseract.
- Save the test image in the same directory.
- Create a variable to store the image using cv2.imread() function and pass the name of the image as parameter.
- Use cv2.imshow(‘window_name’, Image_name).
- To return coordinates pytesseract.image_to_boxes (‘image_name’) and store it in a variable.
- Print the string.
- Add a cv2.waitKey(0) to display image for infinity.
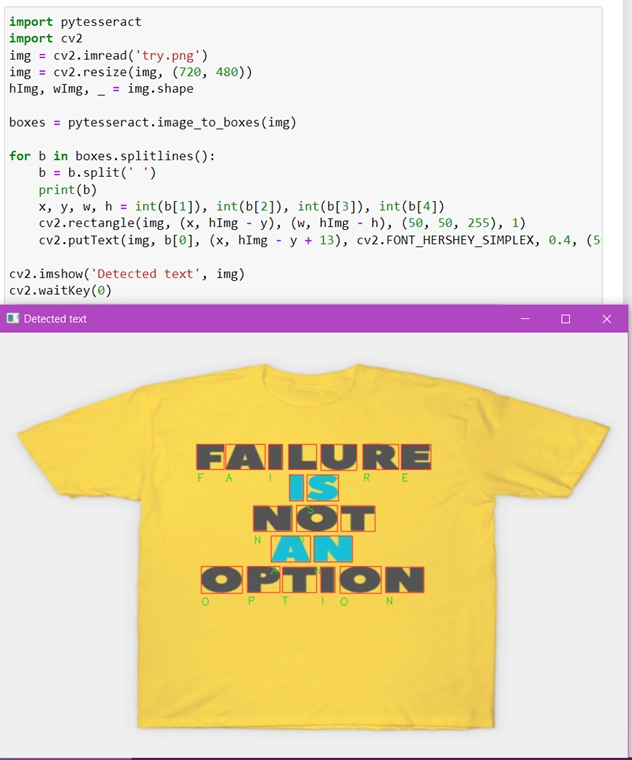
DRAW BOXES AROUND THE DETECTED CHARACTERS AND LABEL THEM
To add boxes around the text and label we need two function of OpenCV:
a) cv2.rectangle(‘image_name’, x_coordinate, y_coordinate, RGB_value_of_color, thickness_of_box)
b) cv2.putText(‘image_name’, x_coordinate, y_coordinate, ‘font_name’, font_size, RGB_value_of_color, thickness_of_text)
- Import pytesseract, cv2.
- Read and show using imread().
- Create two variables to store the dimensions of each character using img.shape().
- Make imaginary text around each character using pytesseract.image_to_boxes(img)
- Create a for loop which converts all the coordinates in the form of list for easy access.
- Initialize four variables for x-coordinate, y- coordinate, width, height.
- Assign their respective values from the above created list.
- As the list elements are in the form of string, convert it to integer.
- Use cv2.rectangle() function to create boxes around the characters.
- Use cv2.putText() to add labels around the characters.
- Use imshow() function to display a final image.
- Add an infinite delay using cv2.waitKey(0).
3. RESULTS
Just as deep learning has impacted nearly every facet of computer vision, the same is true for character recognition and handwriting recognition. Deep learning based models have managed to obtain unprecedented text recognition accuracy, far beyond traditional information extraction and machine learning image processing approaches.
Tesseract performs well when document images follow the next guidelines:
• Clean segmentation of the foreground text from background
• Horizontally aligned and scaled appropriately
• High-quality image without blurriness and noise
The latest release of Tesseract 4.0 supports deep learning based OCR that is significantly more accurate. The OCR engine itself is built on a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) network, a kind of Recurrent Neural Network (RNN).
Tesseract is perfect for scanning clean documents and comes with pretty high accuracy and font variability since its training was comprehensive. I would say that Tesseract is a go-to tool if your task is scanning of books, documents and printed text on a clean white background.





Top comments (2)
Hello, I need Python OpenCV developer.
Kindly contact me
Hi, how can i help you ?