Without Z-index (Default order)
Reference: Stacking without the z-index property - CSS: Cascading Style Sheets | MDN
The number(#) is the order of appearance in the HTML

Main points
- Elements are rendered in the order of appearance in the HTML
- Positioned elements come on top of non-positioned elements (#5 comes the very bottom)
Using Z-index
Reference: Using z-index - CSS: Cascading Style Sheets | MDN
Main points
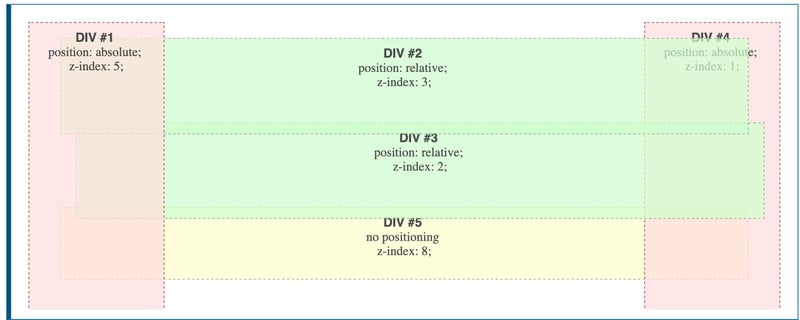
- The higher
z-indexelements comes on top - If the z-index of element doesn't have a positioned element(*),
z-indexdoes NOT have an effect => No stacking context is created(More on the next section)
(* ☝️ above is not precise. flex item and grid item don't need to be positioned to use z-index. Please refer to this link for when the stacking context is created)
- No
z-indexmeansz-index: auto
The stacking context
Reference: The stacking context - CSS: Cascading Style Sheets | MDN
Main points
- Elements are grouped into stacking contexts
-
z-indexvalue is only compared against other elements in the same context => (DIV#4 has the highest z-index of all DIVs, but it is compared within the same stacking context)






Top comments (2)
No z-index means z-index: 0 --> no, it means z-index:auto and not 0. There is a difference because 0 create a stacking context while auto doesn't.
If the z-index of element doesn't have a positioned element, z-index does NOT have an effect --> flex item and grid item don't need to be positioned to use z-index
Thanks a lot for your comment!!
Updated the content!