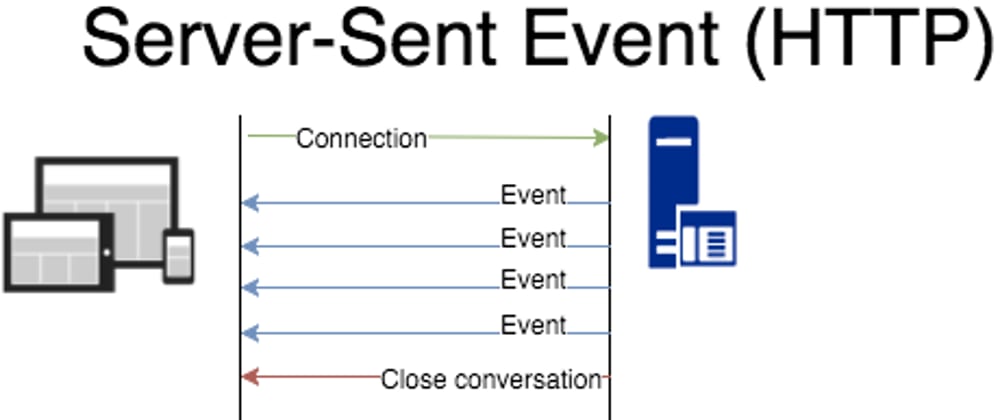
Server-Sent Events (SSE) is a server push technology enabling a client to receive automatic updates from a server via HTTP connection, and describes how servers can initiate data transmission towards clients once an initial client connection has been established.
Server Sent Event is a good choice when we need to notify the browser.
-- wikipedia
If you're working with Amazon API Gateway and WebSocket in order to notify your clients this connection can be more expensive.
SSE can be a good choice when our application needs to send a message to it's clients.
This is a simple example how we can implementing SSE in Go.
//main.go
package main
import (
"bytes"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"math/rand"
"net/http"
"time"
"github.com/gofiber/adaptor/v2"
"github.com/gofiber/fiber/v2"
)
type Client struct {
name string
events chan *DashBoard
}
type DashBoard struct {
User uint
}
func main() {
app := fiber.New()
app.Get("/sse", adaptor.HTTPHandler(handler(dashboardHandler)))
app.Listen(":3000")
}
func handler(f http.HandlerFunc) http.Handler {
return http.HandlerFunc(f)
}
func dashboardHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
client := &Client{name: r.RemoteAddr, events: make(chan *DashBoard, 10)}
go updateDashboard(client)
w.Header().Set("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "*")
w.Header().Set("Access-Control-Allow-Headers", "Content-Type")
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "text/event-stream")
w.Header().Set("Cache-Control", "no-cache")
w.Header().Set("Connection", "keep-alive")
timeout := time.After(1 * time.Second)
select {
case ev := <-client.events:
var buf bytes.Buffer
enc := json.NewEncoder(&buf)
enc.Encode(ev)
fmt.Fprintf(w, "data: %v\n\n", buf.String())
fmt.Printf("data: %v\n", buf.String())
case <-timeout:
fmt.Fprintf(w, ": nothing to sent\n\n")
}
if f, ok := w.(http.Flusher); ok {
f.Flush()
}
}
func updateDashboard(client *Client) {
for {
db := &DashBoard{
User: uint(rand.Uint32()),
}
client.events <- db
}
}
// JS client
const source = new EventSource("http://localhost:3000/sse")
source.onmessage = (event) => {
console.log("OnMessage Called:")
console.log(event)
console.log(JSON.parse(event.data))
}






Top comments (2)
Nice
Thanks for the post.
Why are you doing a keepalive every second?