The BJT was initially designed in 1948 and has helped in redesigning the technological realm and our daily lives. The BJT utilizes both subatomic particles and ports as electricity transporters. FETs employ some sort of electricity transporter thanks to their indifference. Amidst the two interconnections, BJT utilizes 2 junction kinds, N-type and P-type, for functioning. The primary aim of a BJT is to hike the rate of electricity; this lets BJTs be utilized as amplifiers or switches, resulting in a wide range of uses in electrical gadgets. NPN and PNP BJTs are the 2 accessible variants of BJTs.
Definition of BJT
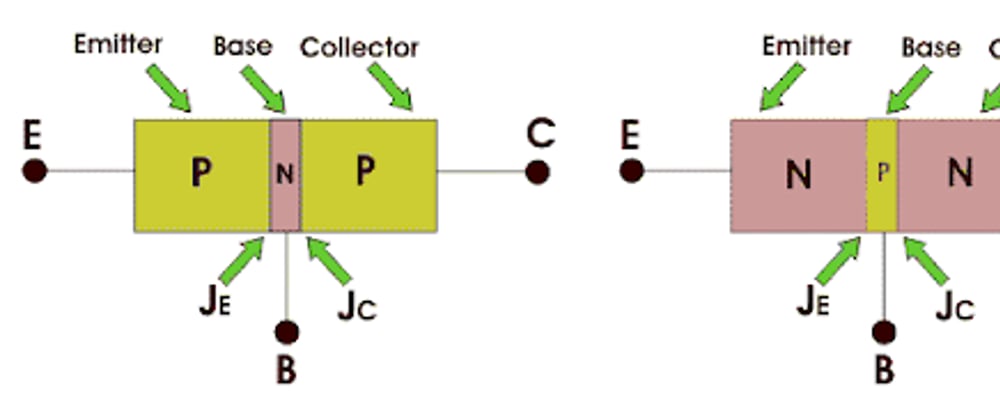
A BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor) is a semiconductor gadget manufactured from 2 PN junctions amidst its architecture and is primarily utilized in amplifying electricity.

Symbol of BJT
The BJT comprises of 3 parts:
- Base
- Emitter
- Collector

The position of the arrow denotes the end for the movement of electricity.
Various types of BJTs have several symbols, so you should not get confused whenever you encounter several ones that are somewhat distinct.
BJT Working
Both the NPN and PNP transistors function similarly, but they differ in how electricity is conducted via voltage transporters dependent on the voltage movement.
The bulk of voltage transporters in the NPN BJT are negatively charged subatomic particles.
The bulk of charge transporters in the PNP BJT are ports.
The electricity movement in a BJT is as a result outnumbered charge transporters, not bulk charge transporters, irrespective of their abundance.
Forward bias is consistently present at the E-B intersection.
Characteristics of BJT
A BJT comprises 3 parts: collector, emitter, and base. We must first understand the functioning modes for BJTs before we can understand their features. The modes includes:
- Common Base
- Common Emitter
- Common Collector
Common Base Characteristics
Input Characteristics
The IE and VCB are the inserted current and voltage for a P-N-P transistor, respectively.Output Characteristics
It illustrates how the output electromotive force and current are linked. The output current, C-B voltage, and IE are all denoted by the letters IC. IE stands for inserted current and functions as a parameter. IE and VEB are positive in bipolar junction transistors, while IC, IB, and VCB are negative.
Common Emitter Characteristics
- Input characteristics For CE mode, IB is the inserted current and VBE is the inserted voltage. As a result, the relationship amids IB and VBE, with VCE as a variable, will be the input characteristics for CE mode.
A forward-biased p-n diode's input characteristics are comparable to those of a CE. However, whenever VCB grows, the early effect shrinks.
- Output Characteristics When the IB is the variable, the output characteristics for CE mode is the graph amid IC and VCE.
CE mode features 3 sections, similar to the output characteristics of common-base transistors:
- active area
- cut-off area
- saturation area
Types of BJT
As we have noticed, a semiconductor features low opposition to transporting current unidirectionally and extreme opposition in the other, and transistors are the semiconductor's gadget mode. The 2 transistors in BJTs are:
- Point contact
- Junction transistor
When 2 transistors are placed in comparison, junction transistors are utilized quite frequently than point type transistors. In addition, junction transistors are divided into 2:
- NPN junction transistors
- PNP junction transistors
NPN Bipolar Junction Transistor
It features a P-type semiconductor crammed amids 2 N-type semiconductors, similar to a cheese slice placed amids 2 sides of a bread.
Conventional guidelines declare that whenever current enters a transistor component, it is classified as positive, and whenever it leaves the part, it is labeled as negative.
An N-P-N transistor, as we all know, is made up of 2 P-N terminals composed by fusing 2 N semiconductors with one a semiconductor. Since it must transfer electricity transporters to the base, the N-type E area is severely high.
Imagine the size of the cheese slice in comparison to buns. The base is not extremely doped and slim in comparison to the E and C. It distributes voltage transporters to the appropriate C.
PNP bipolar junction transistor
The emitter is more positive thanks to the base and also with regard to the collector in PNP. It is utilized for regulatory and heightening purposes. The C end is normally linked to a positive supply, while the E is linked to a negative contribution via a resistor in either the E or C system.
Applications of BJT
High driving capacity:
It is capable of driving at a high speed. Devices are coupled in series and parallel, respectively, for high electromotive force or electricity handling capacity. Moreover, the ability of individual gadgets to drive is frequently acknowledged.
Oscillation circuit:
Oscillation circuits are favored.
Clippers:
BJTs can be used to change the shape of waves in clipping circuits. This can be used as a basic diode for clipping, however diodes have the drawback of being uncontrollable.
Demodulator and modulator:
BJTs can be utilized in circuits for demodulation and modulation. BJTs are still utilized in the “Amplitude modulation” technique, which is a very old known modulation technique.
Circuits for detection:
BJTs can be utilized in systems for detection. A new semiconductor sensor type for monitoring ionization radiation dosage.
Amplifiers:
Amplification, in which BJTs are employed in the amplifier's circuit to magnify tiny signals, is one of the most crucial utilizations of BJTs. These small parts, found in audio amplifiers, enhance very low audio impulses to audible levels.

Electrical switch:
You can utilize it as an electrical switch as they are crucial when changing the end of DC and AC charge in inverters.
Automatic switch:
In an electrical circuit, an automatic switch could be utilized rather than a manual switch. Because detector output indicators are minute, sometimes worthless in electronic systems. However, if these indications are utilized to drive BJTs, they will be useful. Because BJT is a low-signal device. These BJT switches could subsequently handle large loads, such as engines.
Conclusion
This concludes our discussion of the BJT. They are widely utilized gadgets for heightening all sorts of electronic indicators in isolated systems built without applying incorporated systems.








Top comments (0)