In this tutorial we will study what is a union in c programming, defining a union, accessing union members variables with the help of a suitable example. So let’s go start.
Union in C Programming
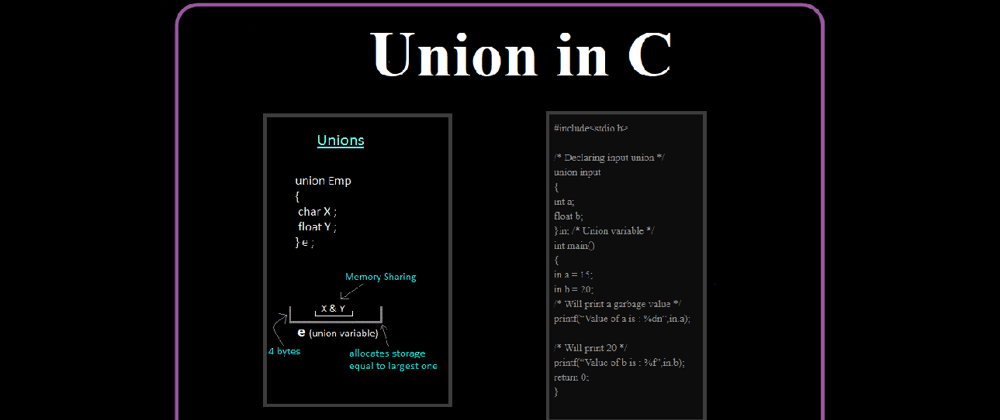
A union is a data type. C Language provides us a special type of data type called union by which it can store many types of data types in the same memory location but it has the same value in the variable of data types at the same time. But the Union can use the same memory location in many types through Union All members of the Union use only one memory location and their size can be as much as the member with the largest size.
Defining a Union
Let's use the union keyword to define unions. This is similar to defining the structure.
The basic syntax of Unions:-
union union_name
{
data_type var1;
data_type var2;
...
...
data_type varn;
}u1.u2,….un;
First of all, union defines keyword and union name. Then before we define variables in curly brackets {}. Then let's create before union variables of curly brackets {}.
union in-put
{
int a;
float b;
}in;
Now it is of in variable input type and it can store an integer value or it can store a float value. We cannot store value in both its variables simultaneously.
Accessing Union Member Variables
Union members also access the same way structure members access. First of all, we write the name of the union. Then before dot (.) An operator is written and the member's name is written. We can assign the value of union members with this type.
in.a = 10;
If we want to print this union member then we can do with these types.
printf(“%d”,in.a);
For Example:-
#include<stdio.h>
/* Declaring input union */
union input
{
int a;
float b;
}in; /* Union variable */
int main()
{
in.a = 15;
in.b = 20;
/* Will print a garbage value */
printf(“Value of a is : %dn”,in.a);
/* Will print 20 */
printf(“Value of b is : %f”,in.b);
return 0;
}
Output
Value of a is: 1101345
Value of b is: 20.00000
I hope that you all liked this tutorial, if you want to read these tutorials more then stay connected with me.
Originally posted on - Union in C Programming






Latest comments (1)
I do appreciate your work on this article! Could you also specify WHY one might need to prefer a union over a struct, for example? I also read the tutorial on UseMyNotes but still cannot grasp the idea of 'why?' - there definitely must be a reason and particular use cases for allocating memory space for only one variable/data type with the largest size. Thank you!